Prostate anatomy
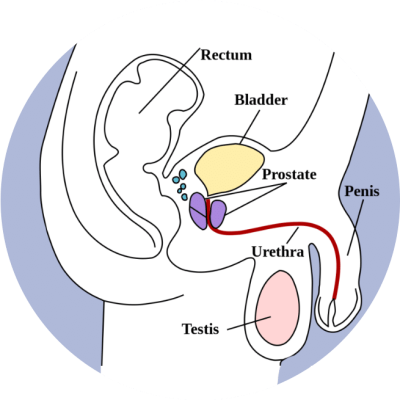
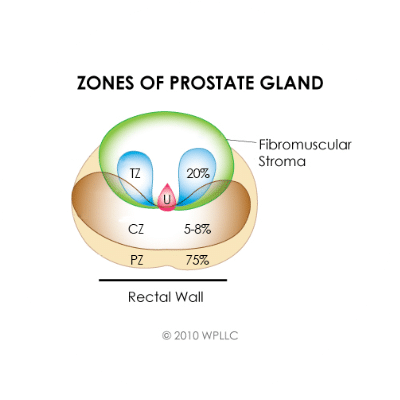
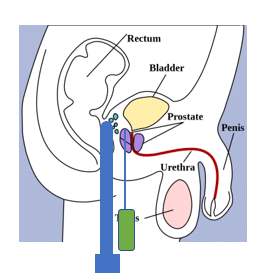
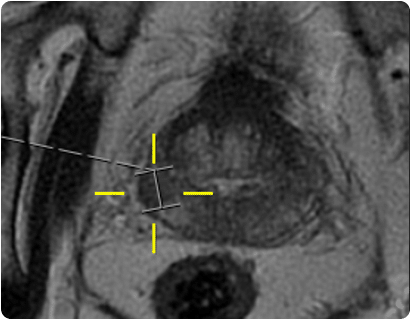
Figure 1
THE CURRENT PROSTATE BRACHYTHERAPY
Prostate cancer is the 2nd most common cancer and 5th leading cause of cancer mortality in men worldwide. Patients with organ-confined disease are appropriately treated with brachytherapy alone. Brachytherapy involves placing multiple, very small, permanent (low dose rate, LDR) or temporary (high dose rate, HDR), radioactive sources into the prostate.
The indications of brachytherapy are ever increasing both as a single treatment (monotherapy) and as a combined therapy, where external beam therapy is used as a boost to brachytherapy. The techniques of brachytherapy have been refined over the last few decades with the introduction of ultrasound guidance to place the sources into the prostate and the introduction of 3D & 4D techniques with real time calculation of dose (dosimetry).
Modern treatment systems have capability, to superimpose planned and implanted seeds, and for real time adjustment of the plan during the implant procedure.
LDR (Low Dose Rate) BRACHYTHERAPY
LDR (Low Dose Rate) BRACHYTHERAPY

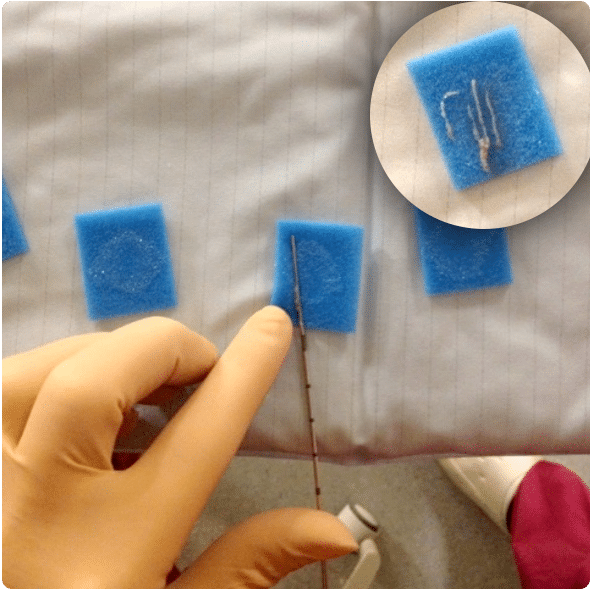
The radioactive sources used for LDR brachytherapy come in the form of seeds, about the size of a grain of rice (fig.3).
Most commonly radioactive iodine-125 (I-125) seeds are used for treatment with some centres opting for palladium-103 (Pd-103). The number of seeds required to deliver the prescribed dose differs between patients primarily based on the size of the prostate and the strength of the seeds.
LDR brachytherapy is sometimes referred to as permanent brachytherapy because the seeds are left in the prostate, delivering dose over a period of a few months. LDR brachytherapy is suitable for cancer that is contained within the prostate gland. It may be used as a single therapy or combined with external beam radiotherapy and/or androgen deprivation therapy.
A device called a ‘stepper unit’ holds a Trans Rectal Ultrasound (TRUS) probe.
Once the patient has been anaesthetised and correctly positioned (lithotomy or extended lithotomy position), the TRUS probe is placed in the rectum and then used throughout the procedure to acquire images of the prostate. Seeds are positioned within the prostate via needles advanced through the perineum. A grid, also mounted on the stepper unit, provides a coordinate system in the x (left/right) and y (anterior/posterior) directions. The z (superior/inferior) depth information is obtained from the stepper unit.
The base of the prostate is identified on the images and this ‘reference depth’ is fed back to the treatment planning software. Needles can be inserted to varying depths relative to this origin. The needles containing the seeds are guided accurately to the correct location using TRUS imaging.
A typical patient set-up can be seen in fig.4
The position of the seeds to be placed in the prostate are carefully planned relative to the patient’s anatomy using treatment planning software packages. Manual and automatic positioning of the seeds are established based on dose calculations in the software, guided by the required prescription dose and dose limitations to organs at risk (urethra and rectum).
European recommendations on permanent seed implantation published in 2000 [2] with a supplement to this in 2007 [3] contain information on the prescription dose for the prostate (145Gy to the whole prostate with 2-3mm margin) and dose limitations for the organs at risk. Similar guidelines have been published by the ABS (American Brachytherapy Society) [2,3,4].
A two stage or single stage approach to implantation may be used:
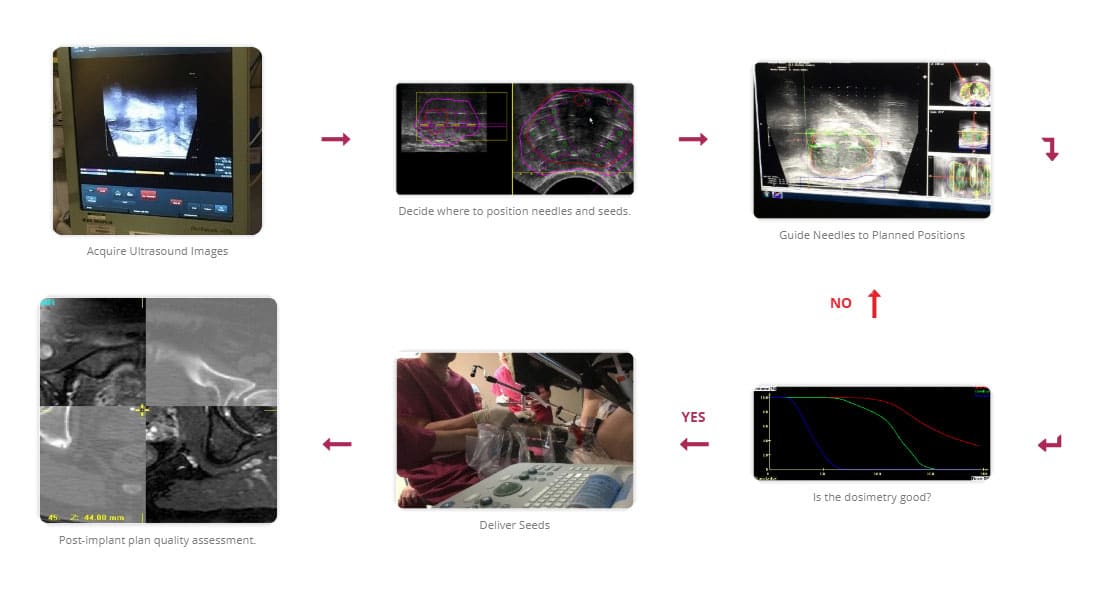
The first step of the two-stage process is to acquire the prostate image data during a TRUS study. This data is then used in an offline planning procedure to produce a treatment plan. The patient then returns to hospital a number of days later, where the setup is replicated, and the seeds are implanted as per the treatment plan.
The single-stage process utilises interactive planning and dynamic dose calculation. During this procedure, the volumetric data are acquired in the same manner as the two-stage technique with the difference now that the plan is computed, and implant performed during the same session. As the seeds are implanted, their actual position is updated and fed back to the planning system where the plan can be re-optimized [5,6]. It has been shown that using this interactive planning technique, produces better coverage of the prostate [7].
An illustration of the single stage procedure can be seen in fig.5.
LDR (Low Dose Rate) BRACHYTHERAPY
HDR (High Dose Rate) BRACHYTHERAPY
The imaging and patient set-up for HDR brachytherapy are very similar to LDR.
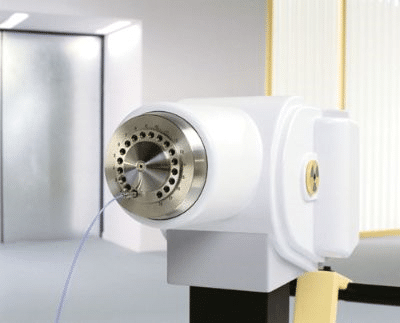
The principle difference between the two techniques is that HDR utilises a single radioactive source (Irridium-192 or Cobalt-60), of much higher energy, which remains in the prostate only temporarily whilst treatment is delivered. As for LDR brachytherapy, the source is advanced into the prostate through needles placed in the perineum. However, for HDR a remote afterloading device (see fig.6) is used to drive the source into multiple positions within each needle, treating one needle at a time, retracting the source, and then moving onto the next. For this reason, HDR brachytherapy is sometimes referred to as temporary brachytherapy. This technique is suitable for treating cancer contained within the prostate or disease that has begun to spread to the seminal vesicles (link to website for prostate anatomy).
The high dose rate of the source used for this technique means that a higher dose can be delivered in a shorter time. The concept is that larger doses per fraction are possible without seriously affecting normal tissues and the radiobiological advantages may be great because the α/β ratio for prostate is low [9].
HDR was initially used as a boost in conjunction with hypofractionated (a shortened treatment schedule) of EBRT (External Beam Radiotherapy) for patients with intermediate- to high-risk disease. More recently, using this method as a monotherapy has been shown to produce good results [10, 11]. There are published guidelines by the GEC-ESTRO group on the recommendations for the treatment of localized prostate cancer with HDR brachytherapy. [12]
The HDR boost technique has been systematically reviewed in a comprehensive article by Zaorsky et al which showed that the standard EBRT dose varies among centres and is generally delivered as a total dose of 36–54 Gy in 1.8- to 2.5-Gy fractions to the prostate, with or without the seminal vesicles; and the HDR boost is typically delivered as a total dose of 12–30 Gy in 1–4 fractions delivered to the prostate alone [13].
The HDR technique offers an extra degree of freedom for confirming the dose and sparing the OARs (organs at risk). This is known as dwell time, the time for which the source remains at each programmed position. Once the needles are placed in the prostate under TRUS (Trans Rectal UltraSound) guidance, highly conformal dose distributions, delivering a high dose to the prostate and significantly lower doses to the rectum and urethra can be achieved.
Due to the radiobiological reasons described above, HDR prostate brachytherapy can be used successfully as monotherapy treatment for low-to-intermediate risk patients [14]. HDR monotherapy has more commonly been delivered in several fractions [15], however, a single fraction of 19- or 20-Gy HDR monotherapy is now being investigated and early data by Hoskin et al have confirmed that single-dose HDR brachytherapy is feasible with acceptable levels of acute complications and suggests that tolerance may have been reached with the single 19-Gy schedule [10].
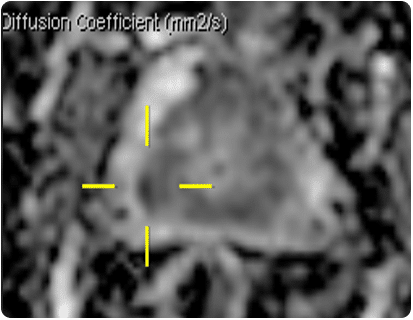
A current area of interest for using HDR techniques within the prostate is that of focal boosts. This is a technique where, in addition to the standard practice of delivering the prescribed dose to the whole prostate, an additional boost dose is given to the dominant intraprostatic lesion (DIL) where it is anticipated that the tumour recurrence is more likely to occur [16]. With advances in high-tech multiparametric MRI (mp-MRI) methods, such as MR spectroscopy and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI together with diffusion-weighted MRI, sensitivity and specificity of prostate cancer detection has improved greatly [17]. Studies have shown that tumour delineation using these techniques has successfully enabled a further boost dose to the DIL of up to 150% of the prescribed dose [18, 19].
LIMITS ON CONVENTIONAL BRACHYTHERAPY AND BIOPSY LEADING TO THE INTRODUCTION OF A ROBOTIC SOLUTION
The limitations of conventional brachytherapy and biopsy techniques which this project will address through the introduction of a robotic solution include:

ACCURACY & SPEED
These often conflict with each other as the need for accuracy slows the procedure. For LDR brachytherapy a 1.0mm error in a single seed position could result in 20% difference in dose at 10mm from the seed however in reality the error is smaller than this as the multiple seeds will be displaced in different directions. Any displacement from the original planned position will deteriorate the quality of the final plan. A slow procedure can lead to complications with equipment if fluid blood tracks into the needles / applicator. Ideally the time under anaesthetic should be short for both the patients’ benefits and throughput for the hospital. A robotic solution removes intra-operator variability and has potential to be consistently quicker than the manual method.

FLEXIBILITY OF SEED / SOURCE POSITION
This should be fully flexible for optimal dose distribution. Whilst with the current technique the needles can be steered to some extent, approximately 2mm in each direction, this is difficult to achieve and may require multiple attempts before achieving the correct needle (and subsequently seed or source) position. This affects the speed of the procedure and is likely to be linked to patient discomfort following the procedure. A robotic solution with needles designed with greater flexibility for steering will address this. Number of punctures: This may be as many as 30 through the perineum (or rectum in the case of trans-rectal biopsies). It is known that the trans-rectal approach has a raised rate of complications relative to the trans-perineal approach [20] and therefore the trans-perineal approach will be used. However the trans-perineal approach can lead to more frequent mild pain post procedure [20] which has the potential to be limited by reducing the number of puncture holes needed in the robotic system to only 1-4 and steering the needle to the required location from here.

QUALITY OF BIOPSY CORES
The current technique can lead to poor quality cores taken by the clinician if the needle is not well positioned or if the biopsy gun is not fired correctly, which leads to increased procedure time. For the pathologists, analysis of prostate cores is more complex if the sample is poor, and in some circumstances, a core may be taken but there is insufficient prostate tissue for analysis.
PROSTATE BIOPSY
Diagnosis of prostate cancer is based on a raised serum PSA (prostate specific antigen) level and/or abnormal findings on digital rectal examination (see fig.7), followed by a prostate biopsy. During the biopsy very small tissue samples are taken from the prostate and analysed by the pathology department to determine if cancer is present and to grade the aggressiveness of the disease.
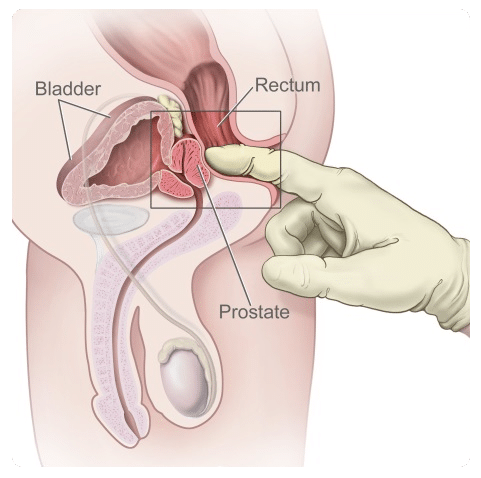
TRUS BIOPSY
(Trans Rectal UltraSound)
Typically, if a patient has obviously palpable cancer they will be referred for a trans-rectal prostate biopsy under local anaesthetic (fig.8). For this procedure the patient lies on their side, knees tucked to chest, and an UltraSound (US) probe is positioned in the rectum giving the practitioner an image of the prostate. A biopsy gun attached to the US probe allows a needle to be fired via the rectum into the prostate extracting a small sample of tissue (see fig.9). The whole procedure takes about 10mins and typically 12 prostate cores are taken.
MP-MRI
(Multi-Parametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
Centres that acquire diagnostic mp-MRIs (see fig.10), report the results using the PIRADS (Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System) system. Typically, if this is reported as showing nothing of concern (PIRADS 1 or 2) then the man is advised that there is an approximately 80% chance that he doesn’t have a significant cancer and future PSA checks are arranged. If there is an obvious lesion (PIRADS 4, 5), he is advised to have a biopsy; trans-rectal if it is thought to be accessible via that route, or trans-perineal if not. Information from the MRI may be utilised during the biopsy either ‘cognitively’, where the Urologist considers the location of the lesion on the MRI and steers the needle specifically towards this region on the UltraSound, or ‘formally’, see explanation below. PIRADS 3 lesions are equivocal and a decision as to biopsy is made on a case by case basis.
TRANS-PERINEAL BIOPSY
A Trans-Perineal biopsy (also referred to as a template biopsy) utilises a set-up equivalent to that used for LDR Brachytherapy.
For this procedure the patient has a general or spinal anaesthetic and as many as 60 cores are taken via the grid and through the perineum (area between anus and scrotum).
This technique may be preferred if part of the prostate cannot be reached with the trans-rectal approach and it avoids puncturing the rectum which is associated with an increased rate of infective complications [20].
FORMAL MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) US (UltraSound) FUSION BIOPSY
A formal fusion biopsy may be used if the lesion is small or difficult to target. The patient setup for this procedure is as for a trans-perineal biopsy. Prior to the biopsy the lesion(s) are marked on the mp-MRIs and these images are registered using specialist software with the US acquired during the biopsy procedure. This image registration allows the marked lesions to be transferred from the MRI to the US and the grid coordinates required to sample cores from the lesions are established (see fig.11).
LIMITS ON EXISTING IMAGE GUIDANCE
At the time of writing multiparametric-MRI (mp-MRI) is increasingly being used as a tool to assist with prostate cancer diagnosis. However, image guidance of needles for biopsy or brachytherapy purposes is still largely UltraSound based. This is because UltraSound images can be acquired quickly and in real-time, allowing the path of the needles and seeds to be visualised as they are steered to the correct location. However, the spatial resolution is a considerable disadvantage at present for UltraSound imaging; most real-time UltraSound shows little to no detail within the prostate capsule making it unsuitable for targeted biopsies or focal brachytherapy (see HDR brachytherapy). With advances in high-tech mp-MRI methods, such as MR spectroscopy and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI together with diffusion-weighted MRI, sensitivity and specificity of prostate cancer detection has improved greatly [17]. Studies have shown that tumour delineation using these techniques has successfully enabled a further boost dose to the DIL of up to 150% of the prescribed dose [18, 19]. Without the use of MRI we are limited in brachytherapy to treating the whole prostate to the same prescription dose. For biopsies we are limited to taking cores systematically throughout the prostate, which in turn requires a larger number of cores to be taken, increasing the number of samples that require analysis and the overall procedure time.
Software exists that enables real-time UltraSound images to be registered with MRI using a variety of techniques to track prostate motion and align the MRI and UltraSound image-sets [21]. This technique however have its limitations as the result of the image registration can depend on the training of the user, the quality of the UltraSound and whether there has been much change to the patient anatomy in the time period between the MR and real-time UltraSound procedure.
In-bore MRI biopsy [22, 23] is in development however this has largely been with a trans-rectal approach which is not suitable for all patients and increases the risk of infection compared to the trans-perineal approach.